5 Interesting Uses of Gold
Gold is one of the most useful minerals that we mine from the Earth. It doesn’t tarnish and is extremely malleable, meaning it is easy to mould into shapes. These are just two of gold’s handy characteristics.
The precious metal has been used for thousands of years to show status and wealth. Today, the most common uses of gold are jewellery, coins and bullion. But we do still use gold for some more special objects. For example, Olympic medals, wedding rings and Oscar awards.
What else is gold used for? Read on to find out about some more interesting uses of gold today.
1. Medicine.
A major benefit of gold is that it can be in contact with the human body and not cause harm to health. Because of this, gold has different forms for use in medicine.

Pain relief is one of the uses of gold in hospitals.
Radioactive gold is used to help diagnose patients. A gold solution passes through the human body. Doctors track the solution, so they are able to spot any problems. Small amounts of gold are in hospital's electronic equipment and life support machines. More about gold in electronics later.
In severe cases of rheumatoid arthritis, gold salts are either taken orally or injected. This is a method to help with pain relief, but it is a slow process. It could take weeks to see a change. Also, the gold isotope, gold-198, is a treatment for cancer.
2. Dentistry.
As gold doesn’t react with the human body, it’s also used in dentistry. Fillings, crowns, bridges and orthodontic appliances contain gold alloys, predominately white gold. The gold used in fillings is typically 15 carat or higher.
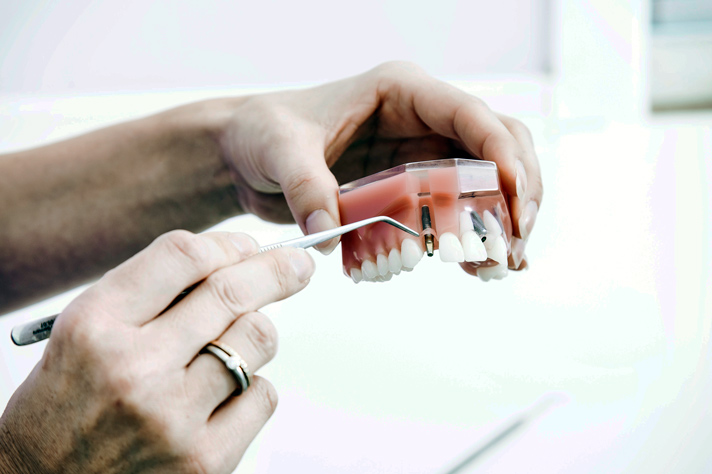
Tooth fillings contain gold.
It has been used in dentistry for 100,000 years. Gold is quite expensive and naturally soft, so it’s obvious to ask, why do we use it on our teeth? Even though gold is delicate, it's very durable. This means that it's long lasting and is able to put up with everything our teeth can.
3. Electronics.
Many electronic devices, i.e. phones, computers, contain a small amount of gold. The devices need rapid and efficient conductors, and gold is perfect for the job!
Corrosion can interrupt the low voltages used by small devices. As gold doesn’t tarnish, it’s extremely useful. It’s used to connect wires, switch and relay contacts.

Electronic devices contain a small amount of gold to help with conductivity.
Each mobile phone contains around 50 milligrams of gold. That's a tiny amount. But when you consider the number of mobiles produced per year, that's over £380 worth of gold just in phones.
4. Space.
Gold is highly reflective of heat and light. There's a thin layer of gold in the visor on an astronaut's helmet. This 0.00005 millimetre film reflects the sun's intense solar radiation. It protects the astronaut's eyes and skin.
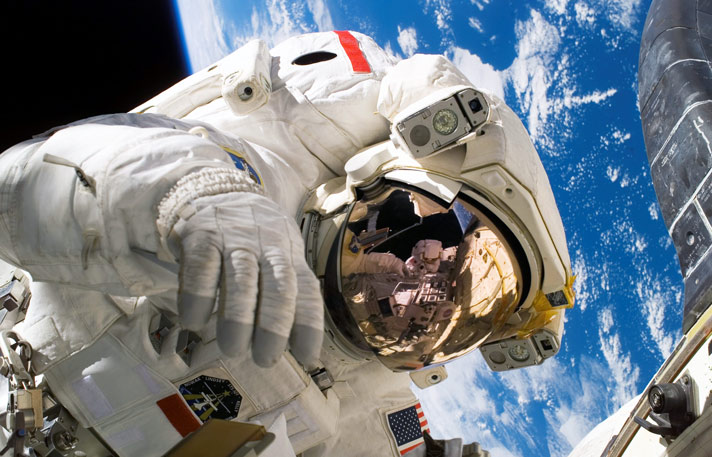

There is gold in the visor to protect from solar radiation.
Another use of gold in space is on all the vehicles sent out into the universe. Each is fitted with a gold coated polyester film. Similar to the visor, this layer of gold reflects infrared radiation. This helps to stabilise the temperature on the spacecraft. Without it, the vehicle would absorb a significant amount of heat.
5. Glass.
Back down on Earth, we also use gold to reflect solar radiation. It’s used in the process of making glass for climate controlled buildings. The small amount of gold in the glass will reflect the solar radiation outwards. This causes the building to be cooler in the summer. But it will reflect the heat inwards in the winter, making the building warmer again.

Buildings with lots of glass widows contain gold to help control the temperature.
Adding different metals to glass creates the colours of stained glass windows. Sulphur makes yellow, Iron makes green and Gold makes red. Gold is suspended in the glass when it is annealed and produces a strong, ruby colour. Red glass is more expensive than any other due to it’s precious metal content.
